|
||
|
With an 8dBi
omni-directional antenna on the AP radio, clients can
associate (on 802.11b/g) from 300 meters
provided the client is in line of site with the mesh
node. If the client device in not in line
of site, the distance decreases to 100-150 meters. Range depends on
connectivity modes.
Clients on 802.11b can achieve twice the range of
802.11g mode.
The range between client and mesh node Access Point (AP) depends largely on whether or not the client is in line of site with the node. Since client radios typically have very small antennas and often hidden inside casings, the client radio is typically not within line of site with the node. Additionally there are usually obstructions (trees, walls) to contend with. Dense trees in between the client and the node, reduces effective range. Trees are soaked with rain, or covered with snow will also decrease effective distance. Walls attenuate signal as well. The degree of attenuation is effected by the thickness and number of walls through which the signal is traveling. Concrete and metal attenuate signals more than wood structures. The effective range of the AP radio to client radio is also dependent upon the desired connectivity of the node-to-client link. For a connectivity of 54 Mbps, clients have to be much closer to the node than for a connectivity of 6 Mbps. Range is also dependent upon the connection rate of the radio link. For a RF connectivity of 54 Mbps (raw), AP radios need to be placed closer together than for a connectivity of 6 Mbps. The table below is the performance characteristics of a 2.4GHz AP radio card. The radio card transmitting at 54 Mbps will output 21 dBm of power. However, at 6 Mbps data rates, the power output increases to 26 dBm or almost quadruple the power. 5 dBm added to the link budget enables more range (at the cost of data rate loss) 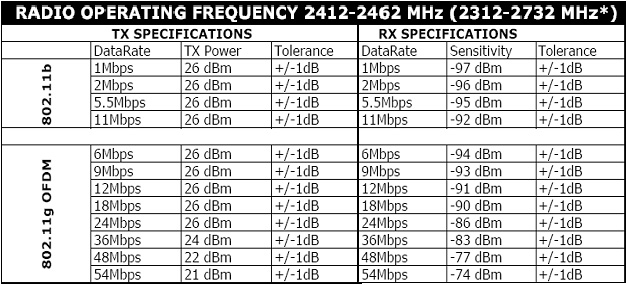 Note also that the receiver in the radio card needs to "hear" a transmitted signal at a minimum of -74 dBm in order to accept a data rate of 54 Mbps. But the card accepts a data rate of 6 Mbps, with a much lower -94 dBm signal. Node-to-node distance varies significantly while still maintaining a "good" connection at different data rates. Range Calculations: A range estimation worksheet is provided for estimating ranges for different antenna gains and usage conditions. Numerous Online RF link budget calculators exist. for example: https://www.pasternack.com/t-calculator-link-budget.aspx Related Links: |
||